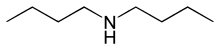
Dibutylamine
Dibutylamine is an amine used as a corrosion inhibitor, in the manufacture of emulsifiers, and as a flotation agent. It is flammable and toxic.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Butylbutan-1-amine | |
| Other names
(Dibutyl)amine Dibutylamine (deprecated) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 506001 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.565 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | dibutylamine |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2248 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H19N | |
| Molar mass | 129.247 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 767 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −61.90 °C; −79.42 °F; 211.25 K |
| Boiling point | 137 to 177 °C; 278 to 350 °F; 410 to 450 K |
| 4.7 g L−1 | |
| Vapor pressure | 340 Pa |
Henry's law constant (kH) |
110 mol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| -103.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.417 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
292.9 J−1 K mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−214.8–−209.8 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−5.6534–−5.6490 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H226, H302, H312, H332 | |
| P280 | |
| Flash point | 40 °C (104 °F; 313 K) |
| 312 °C (594 °F; 585 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.1–10% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
360 mg kg−1 (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
Related amines |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3–160, 5–54, 8–53, 8–112, 15–18, 16–27, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- Gangolli, S. (1999). The Dictionary of Substances and Their Effects. London: Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 204. ISBN 9780854048137. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.