Dibromoiodoethylene
Dibromoiodoethylene is a dense organic liquid consisting of an ethylene core with two bromine atoms and one iodine atom as substituents. It is formed by the reaction of dibromoacetylene with hydrogen iodide.[1]
| |||
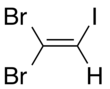 1,1- isomer | |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2HBr2I | |||
| Molar mass | 311.742 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
There are three isomers of dibromoiodoethylene, varying in the position of the two bromine atoms compared to each other.
References
- Sartori, Mario (1939). The War Gases Chemistry and Analysis. Translated by L. W. Marrison. New York: D. Van Nostrand Co., Inc. p. 51.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
-1%252C2-Dibromo-1-iodoethene.png.webp)
-1%252C2-Dibromo-1-iodoethene.png.webp)