Dibenzoylhydrazine
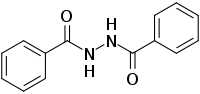
Dibenzoylhydrazine (DBH) is a synthetic chemical compound with the chemical formulation C14H12N2O2. It is sometimes known as a benzoic acid amine, and is related to benzoyl peroxide, tricarban, isocarboxazid, and hydrazine. The substance was patented as an "ecdysone receptor ligand-binding domain structure" on 9 December 2004 by Michael C. Lawrence and nine others at the Australian CSIRO,[1] and since 1991 it had been known to be effective in compound form against insect pests of the orders Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, and Hemiptera.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N′-Benzoylbenzohydrazide | |
| Other names
1,2-Dibenzoylhydrazine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 523810 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.209 |
| EC Number |
|
| 281733 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H12N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 240.262 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Tebufenozide, methoxyfenozide and halofenozide are classed as commercial DBHs.[3]
In 2013, a compound of the substance was tested with promising results against larvae of Anopheles gambiae, the major vector for human malaria.[3]
References
- "Ecdysone receptor ligand-binding domain structure", WO 2004106374 A1
- "Dibenzoylhydrazine compound and insecticide", JPH03145447A
- "A new dibenzoylhydrazine with insecticidal activity against Anopheles mosquito larvae", Pest Manag Sci. 2013 Jul;69(7):827-33. doi: 10.1002/ps.3441