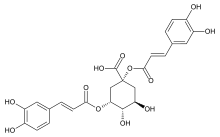
Cynarine
Cynarine is a hydroxycinnamic acid derivative and a biologically active chemical constituent of artichoke (Cynara cardunculus).[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,3R,4S,5R)-1,3-Bis{[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid; Cynarin; Cinarin; Cinarine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H24O12 | |
| Molar mass | 516.455 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Chemically, it is an ester formed from quinic acid and two units of caffeic acid.
See also
References
- Panizzi, Luigi; Scarpati, Maria Luisa (1954). "Constitution of Cynarine, the Active Principle of the Artichoke". Nature. 174 (4440): 1062–3. doi:10.1038/1741062a0. PMID 13214078. S2CID 4254603.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.