Cyclopyrrolones
Cyclopyrrolones are a family of hypnotic and anxiolytic nonbenzodiazepine drugs with similar pharmacological profiles to the benzodiazepine derivatives.
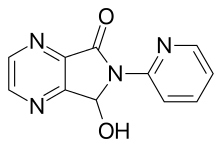
Skeletal formula of the parent compound, cyclopyrrolone
Although cyclopyrrolones are chemically unrelated to benzodiazepines, they function via the benzodiazepine receptor of neurotransmitter GABA.[1] The best-known cyclopyrrolone derivatives are zopiclone (Imovane) and its active single-enantiomer component, eszopiclone (Lunesta), which are used to treat insomnia, and have a known potential for abuse. Other cyclopyrrolones include:
- Pagoclone – anxiolytic
- Pazinaclone – anxiolytic
- Suproclone – anxiolytic
- Suriclone – anxiolytic
References
- Jones, Ian R; Sullivan, Gary (January 10, 1998). "Physical dependence on zopiclone: case reports". The BMJ. 316 (117). doi:10.1136/bmj.316.7125.117. Retrieved April 21, 2021.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.