Cupey, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Cupey is one of the 18 barrios of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico located in the mountainous area of the municipality. It is the largest barrio or district in the San Juan and the third most populous with 32,833 inhabitants according to the 2020 US Census.[3] The territorial land area of Cupey is 7.49 square miles (19.40 km2). It is bound by the municipality of Caguas to the South, by the municipality of Trujillo Alto to the East, by the barrios of Caimito and Monacillo to the West, and by the barrios of El Cinco and Sabana Llana Sur to the North. Between 1990 and 2000 Cupey had a 17.98% increase in population, more than any other barrio in San Juan.
Cupey | |
|---|---|
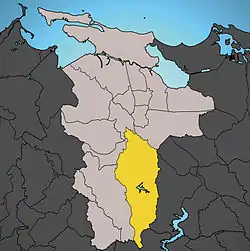 Location of Cupey shown in yellow | |
| Coordinates: 18°20′43″N 66°03′06″W[1] | |
| Commonwealth | |
| Municipality | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 7.57 sq mi (19.6 km2) |
| • Land | 7.50 sq mi (19.4 km2) |
| • Water | 0.07 sq mi (0.2 km2) |
| Elevation | 381 ft (116 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 32,833 |
| • Density | 4,300/sq mi (1,700/km2) |
| 2020 census | |
| ZIP Code | 00926 |
History
Established in 1878, this barrio was a former ward of the now defunct town of Río Piedras.[4] It was divided into the subbarrios of Cupey Alto and Cupey Bajo. It is named for the Cupey tree, sometimes spelled copey (Clusia rosea), which is indigenous to the Caribbean. It belongs to the family Clusiaceae. Linguistically, cupey or copey most likely come from the Taino language (cubey) and might or might not share a lexical relation to the name Cuba.[5]
The barrio was in Spain's gazetteers[6] until Puerto Rico was ceded by Spain in the aftermath of the Spanish–American War under the terms of the Treaty of Paris of 1898 and became an unincorporated territory of the United States. In 1899, the United States Department of War conducted a census of Puerto Rico finding that the population of Cupey barrio was 1,834.[7]
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 1,834 | — | |
| 1910 | 2,109 | 15.0% | |
| 1920 | 2,562 | 21.5% | |
| 1930 | 2,928 | 14.3% | |
| 1980 | 27,739 | — | |
| 1990 | 31,072 | 12.0% | |
| 2000 | 36,659 | 18.0% | |
| 2010 | 36,058 | −1.6% | |
| 2020 | 32,833 | −8.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1899 (shown as 1900)[8] 1910-1930[9] 1930-1950[10] 1980-2000[11] 2010[12] 2020[13] | |||
In 1956, the Puerto Rico Legislature integrated the town of Río Piedras and the town of San Juan. Today, Cupey is the largest barrio in San Juan in area.
Landmarks
The Interamerican University of Puerto Rico's Metropolitan Campus, and the Metropolitan University, a unit of the Ana G. Méndez University System, are located in Cupey.
TV personality and astrologer, Walter Mercado, is buried at Señorial Memorial Park in Cupey.[14]
 Señorial Memorial Park and Funeral Home in Cupey
Señorial Memorial Park and Funeral Home in Cupey
Geography
Cupey barrio is 7.49 square miles (19.40 km2). It is bound to the north by the San Juan barrios of El Cinco along State Road PR-176, and by Sabana Llana Sur in the Venus Gardens neighborhood. From the south it is bound by the municipality of Caguas, starting at the intersection of state roads PR-176 and PR-175. From the east it is bound by the town of Trujillo Alto along state road PR-199. From the west it is bordered by the San Juan wards of Caimito, starting at the intersection of state road PR-199 and state highway PR-52, and by Monacillo.
San Juan's only lake, Lago Las Curias, is located in Cupey. It was originally dammed in 1946 by the Municipal Government of San Juan to provide potable water to the cities of Río Piedras and San Juan and was later transferred to the Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority (PREPA). it is currently owned by the Puerto Rico Aqueducts and Sewer Authority (PRASA). The earthen dam is approximately 75 feet high and 800 feet long and its design capacity is 1,120 acres-feet.[15]
Notable residents
- Cheo Feliciano, salsa legend
- Raul Julia, actor
- Rafael Hernández, composer and musician
- Lolita Lebrón, Puerto Rico Nationalist leader
- Kenneth McClintock, Secretary of State and Senate President
- Thomas Rivera Schatz, Senate President
- Jorge Santini, Mayor of San Juan
- Félix Trinidad, world champion boxer, member of the International Boxing Hall of Fame
- Felix Trinidad Sr., Puerto Rico national Featherweight boxing champion
- Walter Mercado, Astrologer, actor, dancer, and writer, best known as a television personality for his shows as an astrologer.
See also
References
- "US Gazetteer 2019". US Census. US Government.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cupey barrio
- "Census profile: Cupey barrio, San Juan Municipio, PR". Census Reporter. Retrieved 2023-09-08.
- Puerto Rico. Office of Historian (1949). Tesauro de datos historicos: indice compendioso de la literatura histórica de Puerto Rico, incluyendo algunos datos inéditos, periodísticos y cartográficos (in Spanish). Impr. del Gobierno de Puerto Rico. p. 306. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- "Dictionary of the Taino Language". www.taino-tribe.org. Retrieved 2021-10-14.
- "Anuario del comercio, de la industria, de la magistratura y de la administración. 1881". Biblioteca Nacional de España (in Spanish). p. 1614. Retrieved 4 April 2023.
- Joseph Prentiss Sanger; Henry Gannett; Walter Francis Willcox (1900). Informe sobre el censo de Puerto Rico, 1899, United States. War Dept. Porto Rico Census Office (in Spanish). Imprenta del gobierno. p. 162.
- "Report of the Census of Porto Rico 1899". War Department Office Director Census of Porto Rico. Archived from the original on July 16, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 3-Population of Municipalities: 1930 1920 and 1910" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 17, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 4-Area and Population of Municipalities Urban and Rural: 1930 to 1950" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 30, 2015. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "Table 2 Population and Housing Units: 1960 to 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 24, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- Puerto Rico: 2010 Population and Housing Unit Counts.pdf (PDF). U.S. Dept. of Commerce Economics and Statistics Administration U.S. Census Bureau. 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-02-20. Retrieved 2019-08-02.
- https://www.census.gov/library/stories/state-by-state/puerto-rico-population-change-between-census-decade.html.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - "Walter Mercado Laid to Rest in Puerto Rico". Entertainment Tonight.
- "REPRESA LAS CURÍAS - Wikimapia". Wikimapia.org. Retrieved 16 August 2016.