Colobonema sericeum
Colobonema sericeum is a species of deep-sea hydrozoan in the family Rhopalonematidae that was first described in 1902.[1] This semi-transparent organism is found in the mesopelagic zone, has 32 tentacles, and has a bell diameter of up 45 mm.[2][3] They are holoplanktonic and never attach to the seafloor as part of their polyp life cycle, but instead have embryos that develop directly into a small, swimming medusae.[3]
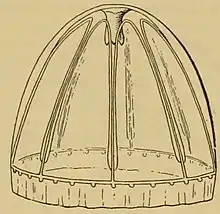
Illustration of Colobonema sericeum
| Colobonema sericeum | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Cnidaria |
| Class: | Hydrozoa |
| Order: | Trachymedusae |
| Family: | Rhopalonematidae |
| Genus: | Colobonema |
| Species: | C. sericeum |
| Binomial name | |
| Colobonema sericeum Vanhöffen, 1902 | |
References
- "Colobonema sericeum Vanhöffen, 1902". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- Hirose, Euichi; Sakai, Daisuke; Iida, Akane; Obayashi, Yumiko; Nishikawa, Jun (2021). "Exumbrellar surface of jellyfish: a comparative fine structure study with remarks on surface reflectance". Zoological Science. 38 (2): 170–178. doi:10.2108/zs200111. PMID 33812356.
- Raskoff, K (2001). "The impact of El Niño events on populations of mesopelagic hydromedusae". Hydrobiologia. 451: 121–129. doi:10.1023/A:1011812812662. S2CID 37298417.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.