Qi Jiguang
Qi Jiguang (Chinese: 戚繼光; pinyin: Qī Jìguāng; Wade–Giles: Ch'i1 Chi4-Kuang1, November 12, 1528 – January 17, 1588),[1][2][3] courtesy name Yuanjing, art names Nantang and Mengzhu, posthumous name Wuyi, was a Chinese military general and writer of the Ming dynasty. He is best known for leading the defense on the coastal regions against wokou pirate activities in the 16th century, as well as for the reinforcement of the Great Wall of China. Qi is also known for writing the military manuals Jixiao Xinshu and Lianbing Shiji or Record of Military Training (練兵實紀), which he based on his experience as a martial educator and defensive planner in the Ming military forces. He is regarded as a hero in Chinese culture.
Qi Jiguang | |
|---|---|
| 戚繼光 | |
 Portrait of Qi Jiguang | |
| Born | November 12, 1528 |
| Died | January 17, 1588 (aged 59) |
| Other names |
|
| Occupation | General |
Biography
Early life
Qi Jiguang was born in the town of Luqiao in Shandong province to a family with a long military tradition. His forefather served as a military leader under the Hongwu Emperor and died in battle. When Zhu Yuanzhang became the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty, he bestowed upon the Qi family the hereditary post of commander-in-chief of Dengzhou Garrison, a district of the present day Penglai.
Qi Jiguang's father Qi Jingtong (戚景通) (1473–1544) was a skilled martial arts expert and an upright and devoted military general. Strongly influenced by his family, Qi Jiguang took an early interest in the military. As a child, he built ramparts from clay, piled up rubble to form barracks, and made flags from bamboo sticks and paper to play war games with his friends and himself as the commander.
When his father died, Qi Jiguang took over the commandership of Dengzhou Garrison at the age of 17. As his siblings were still young, he married Lady Wang and left domestic affairs to her. Besides building up the naval defense at the garrison, he also led his troops in the defense of Jizhou (薊州, east of present-day Beijing) against Mongol raiders during spring time from 1548 to 1552.
At the age of 22, Qi Jiguang headed for Beijing to take part in the martial imperial examination. During this time, Mongol troops led by Altan Khan broke through the northern defenses and laid siege to Beijing. Candidates participating in the martial arts exam were mobilized to defend the nine gates of the capital. Qi Jiguang twice submitted defense proposals to the emperor and was noted to have displayed extraordinary valor and military cunning during the battle, and saw the defeat of the invaders.
Battles against the wokou pirates
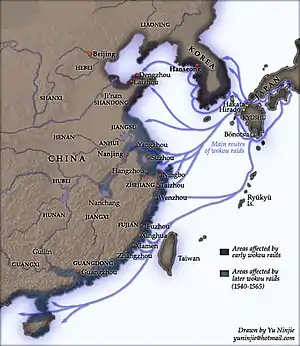
In 1553, Qi Jiguang was promoted to Assistant Regional Military Commissioner (都指揮僉事) of Shandong's defense force against wokou pirates. The marauders that terrorized the Eastern coastlines were hardly pirates. They constructed inland bases on land and besieged walled cities. They conducted continuous raids for at least two decades. Additionally, they weren't just Japanese. Most of the time, they worked together with mixed Chinese bands, with the latter frequently dominating. Even Chinese explorers provided their leadership. However, the Japanese pirates were the main combatants. Japan served as the base of the invasion, and the Japanese provided all military expertise and equipment.[4]
When Qi Jiguang took over the command of Shandong's coastal defense, he had less than 10,000 troops at hand, though the recorded strength was 30,000. Furthermore, many of his soldiers who were young and strong men deserted to make a living elsewhere, leaving behind the old and the weak. The troops also lacked training and discipline, while the defense works were dilapidated due to years of negligence.
In the fall of 1555, Qi was sent to Zhejiang where the pirating situation had spiraled out of control. Together with two other generals, Yu Dayou and Tan Lun, Qi led Ming forces to a decisive victory at Cen Harbor (岑港) in 1558. Henceafter, his troops continued to deal blows to the pirates at Taozhu (桃渚), Haimen Garrison and Taizhou. After the victory at Cen Harbor, not only was Qi not credited for his valor, he was almost demoted over slander that he liaised with wokou pirates.
With the situation in Zhejiang under control, Qi shifted his focus to drilling his soldiers. He drafted mainly miners and farmers from the county of Yiwu because he believed these people to be honest and hardworking. He also oversaw the construction of 44 naval vessels of various sizes to be used against pirates at sea.
The first trial for Qi's new army came in 1559. After a month-long battle with wokou pirate in Taizhou Prefecture, the pirates suffered over 5,000 casualties, while Qi's army established a name for itself among both the people of Zhejiang and its enemies. Partly as a result of Qi's military success in Zhejiang, pirate activities surged in the province of Fujian. More than 10,000 pirates had established strongholds along the coast from Fu'an in the north to Zhangzhou in the south.
In July 1562, Qi Jiguang led 6,000 elite troops south into Fujian. Within two months, his army had eradicated three major lairs of wokou pirates at Hengyu (橫嶼), Niutian (牛田) and Lindun (林墩). However, his own army also suffered significant losses of nearly a hundred men due to fighting and disease.
Seeing the pirate infestation in Fujian subdued, Qi then returned to Zhejiang to regroup. The pirates took the opportunity to invade Fujian again, this time succeeding in conquering Xinghua (興化, present day Putian).
In April 1563, Qi Jiguang led 10,000 troops into Fujian and reclaimed Xinghua. Over the next year, a series of victories by Qi Jiguang's army finally saw the pirate problem in Fujian resolved.
In September 1565, a major battle against wokou pirates was fought on the island of Nan'ao, which lies near the boundary between the provinces of Fujian and Guangdong. There Qi joined arms with his old comrade Yu Dayou again to defeat the remnant of the combined Japanese and Chinese pirate force.
Years on the northern frontier

After eliminating the pirate threat, Qi Jiguang was called to Beijing in late 1567 to take charge of training the imperial guards.
With the revolt against the Yuan dynasty in mid-14th century, the Hongwu Emperor drove the Mongols north beyond the Great Wall and founded the Ming dynasty. However, he did not manage to eliminate Mongolian power, which continued to pester the northern frontier for the next two hundred years. When Qi was in Beijing in 1550, Altan Khan, ruler of the Tumed Mongols, broke through the northern defenses and nearly devastated Beijing. In 1571, the Ming dynasty bestowed the title "Lord Shunyi" (順義王) upon Altan Khan and established trade with the Mongols. Altan Khan then forbade his subordinates from raiding Chinese settlements. However, other Mongols led by Jasaghtu Khan continued to test Qi's defenses, though without much success.

In the next year, he was given command of the troops in Jizhou to defend against the Mongols. Qi oversaw the repair work on the segment of the Great Wall between Shanhai Pass and Juyong Pass. He also directed the construction of watchtowers along the wall. After two years of hard work, more than 1,000 watchtowers were completed, giving the defensive capability in the north a great boost.
In the winter of 1572, Qi also conducted a month-long military exercise involving more than 100,000 troops. Based on his experience with the exercise he wrote the Records of Military Training (練兵實紀), which became an invaluable reference for military leaders after him.
During the early reign of the Wanli Emperor (1570s), the Mongol army led by Dong Huli, chieftain of the Duoyan tribe, continuously invaded the Ming territory. Qi Jiguang's troops defeated them many times and captured Dong Huli's younger brother Changtu. When Dong Huli brought his nephew and 300 clansmen to beg tearfully for mercy at the outpost, Qi Jiguang accepted their surrender. Dong released captives from his previous plunders and vowed to never invade Jizhou again.
Death
Qi was politically connected to Zhang Juzheng and fell out of favor with the Wanli Emperor after the death of Zhang. In early 1583, Qi was relieved of his duty. His wife left him soon after and he spent the rest of his years in poverty and ailing health.[5]
He died on 17 January 1588.[5]
Legacy

Books by Qi Jiguang
Qi Jiguang documented his ideas and experience in the form of two books on military strategy, the Ji Xiao Xin Shu (紀效新書) and the Lianbing Shiji (練兵實紀) or Record of Military Training. He also wrote a great number of poems and proses, which he compiled into the Collection of Zhizhi Hall (止止堂集), named after his study hall during his office in Jizhou.
Guangbing
A type of hard pancake called guangbing (光餅, Foochow Romanized: guŏng-biāng, known as kompyang in Malaysia and Indonesia) was named after Qi Jiguang.
Ships named in honor Qi
The Republic of China Navy Cheng Kung class frigate Chi Kuang (FFG 1105) as well as the People's Liberation Army Navy Type 680 training ship Qi Jiguang are after him.
In popular culture
A Taiwanese film 1978 Qi Jiguang (戚繼光) (English title Great General) depicts the conflict with the pirates.[6]
Qi Jiguang's late years in Shandong are the subject of the 1980 Hong Kong film, The Warrant of Assassination (密殺令).[7]
The 2008 Chinese television series The Shaolin Warriors provided a fictional account of Qi Jiguang enlisting the help of Shaolin Monastery's warrior monks in defending China from the wokou and other invaders. Malaysian actor Christopher Lee played Qi Jiguang.
In 2017 the film God Of War[8] is another fictional portrayal of the General and his wife, with Vincent Zhao in the leading role.
A historical portrayal of Qi Jiguang by actor Yu Beng Lim is represented in the 2007-2008 joint Discovery Channel and Channel 4 special Behind the Great Wall[9]/ The Great Wall of China.[10] The documentary focuses on Qi's rebuilding of the Great Wall through his partnership with Senior Grand Secretary Zhang Juzheng.
References
- Millinger & Fang 1976, p. 220
- Huang 1981, p. 156
- Gyves 1993, p. 15
- https://archive.org/details/1587yearofnosign00huan/page/162/mode/2up?q=japanese+pirates
- Hawley 2005, p. 56.
- "戚繼光 (1978) Great General". hkmdb.com. Retrieved March 9, 2020.
- "The Warrant of Assassination". Hong Kong Movie Database.
- Dang kou feng yun (2017)
- "Discovery Channel's Original Special, BEHIND THE GREAT WALL, Tells the Story of the Greatest Architectural Structure Ever Built and How It Defined Ruler and People of the Ming Dynasty (summary only)".
- The Great Wall of China (TV Movie 2007) - IMDb, retrieved 2022-01-28
Bibliography
- Millinger, James F.; Fang, Chaoying (1976), Goodrich, L. Carrington; Fang, Chaoyang (eds.), Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368-1644, vol. 1, New York: Columbia University Press, pp. 220–224, ISBN 978-0-231-03833-1
- Hawley, Samuel (2005), The Imjin War, The Royal Asiatic Society, Korea Branch/UC Berkeley Press, ISBN 89-954424-2-5
- Huang, Ray (1981), 1587, a Year of No Significance: The Ming Dynasty in Decline, New Haven: Yale University Press, ISBN 978-0-300-02518-7
- Gyves, Clifford M. (1993), An English Translation of General Qi Jiguang's "Quanjing Jieyao Pian" (PDF), University of Arizona, archived (PDF) from the original on November 9, 2013