Cartesian theater
"Cartesian theater" is a derisive term coined by philosopher and cognitive scientist Daniel Dennett to refer pointedly to a defining aspect of what he calls Cartesian materialism, which he considers to be the often unacknowledged remnants of Cartesian dualism in modern materialist theories of the mind.
Overview
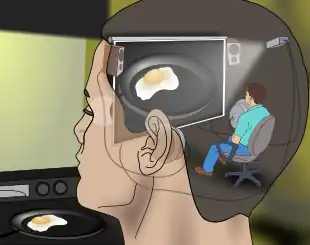
Descartes originally claimed that consciousness requires an immaterial soul, which interacts with the body via the pineal gland of the brain. Dennett says that, when the dualism is removed, what remains of Descartes' original model amounts to imagining a tiny theater in the brain where a homunculus (small person), now physical, performs the task of observing all the sensory data projected on a screen at a particular instant, making the decisions and sending out commands (cf. the homunculus argument).
The term "Cartesian theater" was brought up in the context of the multiple drafts model that Dennett posits in Consciousness Explained (1991):
Cartesian materialism is the view that there is a crucial finish line or boundary somewhere in the brain, marking a place where the order of arrival equals the order of "presentation" in experience because what happens there is what you are conscious of. ... Many theorists would insist that they have explicitly rejected such an obviously bad idea. But ... the persuasive imagery of the Cartesian Theater keeps coming back to haunt us—laypeople and scientists alike—even after its ghostly dualism has been denounced and exorcized.
— Daniel Dennett, Consciousness Explained [p.107, original emphasis.][1]
See also
Notes
- Daniel C Dennett. (1991), Consciousness Explained, Little, Brown & Co. USA (ISBN 0-316-18065-3)
References
- Dennett, D. and Kinsbourne, M. (1992) "Time and the Observer: the Where and When of Consciousness in the Brain". (1992) Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 15, 183-247, 1992. Reprinted in The Philosopher's Annual, Grim, Mar and Williams, eds., vol. XV-1992, 1994, pp. 23–68; Noel Sheehy and Tony Chapman, eds., Cognitive Science, Vol. I, Elgar, 1995, pp. 210–274.
