Camembert
Camembert (/ˈkæməmbɛər/, also UK: /-mɒmbɛər/, French: [kamɑ̃bɛʁ] ⓘ) is a moist, soft, creamy, surface-ripened cow's milk cheese. It was first made in the late 18th century in Camembert, Normandy, in northwest France. It is sometimes compared in look and taste to brie cheese, albeit with a slightly lower butterfat content than brie's [1] typical 60% and 75%[2] by weight.
| Camembert | |
|---|---|
_11.jpg.webp) | |
| Country of origin | France |
| Region, town | Normandy, Camembert |
| Source of milk | Cows |
| Pasteurized | Not traditionally |
| Texture | Soft-ripened |
| Aging time | At least 3 weeks |
| Certification | Camembert de Normandie AOC 1983, PDO 1992 |
Production
The first camembert was made from unpasteurized milk, and the AOC variety "Camembert de Normandie" (approximately 10% of the production) is required by law to be made only with unpasteurized milk. Many modern cheesemakers outside of Normandy, France, however, use pasteurized milk for reasons of safety, compliance with regulations, or convenience.[3]
The cheese is made by inoculating warmed cow milk with mesophilic bacteria, then adding rennet and allowing the mixture to coagulate. The curd is then cut into roughly 1 cm (1/2 inch) cubes, salted, and transferred to low cylindrical camembert molds.[3] The molds are turned every six to twelve hours to allow the whey to drain evenly from the cut curds; after 48 hours, each mold contains a flat, cylindrical, solid cheese mass weighing generally 250 grams (about 9 oz). At this point the fresh cheese is hard, crumbly, and bland.
The surface of each cheese is then sprayed with an aqueous suspension of the mold Penicillium camemberti, and the cheeses are left to ripen for a legally required minimum of three weeks. This affinage produces the distinctive bloomy, edible rind and creamy interior texture characteristic of the cheese.[3] Once the cheeses are sufficiently ripe, they are wrapped in paper and may be placed in wooden boxes for transport.

History
Camembert was reputedly first made in 1791 by Marie Harel, a farmer from Normandy, following advice from a priest who came from Brie.[4] She is credited with having refined a previously existing cheese recipe from the Pays d'Auge region and having launched it into the wider world.[5] She passed her secrets on to her daughter, whose husband, Victor Paynel, presented one of his wife's best cheeses to Napoleon III, who gave to it his royal seal of approval.[5]
The origin of the cheese known today as Camembert is more likely to rest with the beginnings of the industrialization of the cheesemaking process at the end of the 19th century.[6] In 1890, an engineer, M. Ridel, devised the wooden box that was used to carry the cheese and helped to send it for longer distances, in particular to America, where it became very popular. These boxes are still used today.
Before fungi were understood, the colour of Camembert rind was a matter of chance, most commonly blue-grey, with brown spots. From the early 20th century onwards, the rind has been more commonly pure white, but it was not until the mid-1970s that pure white became standard.
The cheese was famously issued to French troops during World War I, becoming firmly fixed in French popular culture as a result. It has many other roles in French culture, literature, and history. It is now internationally known, and many local varieties are made around the world.
The variety named Camembert de Normandie was granted a protected designation of origin in 1992 after the original AOC in 1983. The AOC Camembert can only be made from raw, unpasteurized milk from Normandes cows. Problems with hygiene regulations have caused restrictions on importation and sale in some countries, notably the US;[7] a variant made from pasteurized milk is sold in these territories instead.
Chemical composition
Camembert cheese gets its characteristic odor from many compounds. These include diacetyl (buttery flavoring for popcorn), 3-methylbutanal, methional (degradation product of methionine), 1-octen-3-ol and 1-octen-3-one (degradation products of fats), phenethyl acetate, 2-undecanone, δ-decalactone, butyric acid, and isovaleric acid,[8] as well as volatile sulfur compounds such as S-Methyl thioacetate.[9]
- Significant contributors to odor of camembert cheese

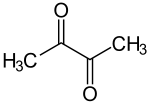
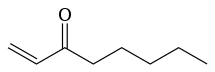
propanal_200.svg.png.webp)
Overripe camembert contains an unpleasant, excessive amount of ammonia, which is produced by the same microorganisms required for ripening.[10]
Comparison to brie
Brie and Camembert are two similar soft cheeses that are both made from cow's milk. Despite their similarities, there are notable differences between them, including their origin, market shape, size, and flavor.
Brie cheese originates from the Brie while camembert comes from Normandy. Traditionally, Brie was produced in large wheels measuring either 22.9 cm (9 in) or 36.8 cm (14.5 in) in diameter.[1] As a result, Brie takes longer to ripen compared to the smaller Camembert cheeses. When sold, Brie is typically cut into segments from the larger wheels, although some variations of Brie are sold as small, flat cylinders. Consequently, the sides of Brie segments are not covered by the rind. On the other hand, Camembert is ripened as a small round cheese measuring 10.2 cm (4 in) in diameter by 3.2 cm (1.26 in) in thickness, and it is fully covered by its rind.[11] This difference in size and rind coverage gives Camembert a slightly stronger flavor compared to Brie ripened for the same duration. Once the rind is cut on Camembert, it typically emits a more pungent aroma than Brie.
In terms of taste, Camembert has a stronger, slightly sour, and sometimes chalky flavor. The texture of Camembert is also softer than that of Brie. When warmed, Camembert becomes creamier, while Brie retains more of its structure when heated. These variations contribute to the contrasting characteristics of the two cheeses.
Packaging

Typically camembert tends to be sold whole in thin, round, wooden containers made from poplar. Modern variations in packaging include cartons and tin cans, with a ring-pull tab for opening (Camembert in metallic boxes does not exist on the French market). The cardboard boxes are reserved for the low-cost camemberts. The product is the same as in the wooden container, wrapped dry in a paper/foil wrapper, and not immersed in brine or oil.
Vegan alternative
Recently, markets and grocers have introduced a vegan alternative to Camembert cheese which is plant-based.[12]
Camembert from other countries
A similar cheese is produced in Hungary under the same name,[13] the Czech Republic under the name Hermelín and in Slovakia as encián or plesnivec. A Camembert-type cheese is also manufactured in Cornwall, UK, and marketed as "Cornish Camembert".[14] Fonterra in New Zealand make a variant called Camembert Log. This is a long cylinder that is about 10 cm (4 in) in diameter and weighs 1 kg (2 lb).[15] Fonterra also make conventional Camembert cheeses under their Mainland, Anchor and Kapiti brand names.[16]
See also
References
- "Brie vs Camembert - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison". Food Struct.
- "Brie Vs. Triple Cream: What are We Even Talking About?". January 18, 2017.
- Smith, Tim (2005). Making artisan cheese : 50 fine cheeses that you can make in your own kitchen. Beverly, Massachusetts: Quarry Books. ISBN 1-59253-197-0.
- "The Invention of Marie Harel, Camembert de Normandie web site". Archived from the original on 2010-01-04. Retrieved 2007-06-21.
- Carr, Sandy (1981). The Simon and Schuster pocket guide to Cheese. New York: Simon and Schuster. p. 44. ISBN 0-671-42475-0. OCLC 7459647.
- Pierre Boisard, Camembert: A National Myth, 2003 ( ISBN 0-520-22550-3 ) claims that Camembert was one of the first globalized, homogenized, and standardized foods.
- Zimberoff, Larissa (2017-06-13). "One of the World's Great Cheeses Might Be Going Extinct". www.bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2019-09-15.
- Kubíckováa, J.; W. Groscha (1998). "Evaluation of Flavour Compounds of Camembert Cheese". International Dairy Journal. 314: 11–16. doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(98)00015-6.
- Martínez-Cuesta MDC, Peláez C, Requena T. Methionine metabolism: major pathways and enzymes involved and strategies for control and diversification of volatile sulfur compounds in cheese. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2013; 53(4): 366-385. doi:10.1080/10408398.2010.536918
- McGee, Harold (2004). On food and cooking: the science and lore of the kitchen. New York: Scribner. ISBN 0-684-80001-2.
- "Camembert vs Brie: What's the Difference". whatdifferencebetween.com. Retrieved 2023-06-15.
- "Nurish camembert style". sainsburys.co.uk. Retrieved 9 May 2023.
- "Camembert in Hungary". Chew.hu. Archived from the original on 2014-06-19.
- "Cornish Camembert". Cornish Country Larder Ltd. Archived from the original on 2015-06-27. Retrieved 2014-11-26.
- Fonterra, Pacific. "Mainland Special Reserve Creamy Camembert Log". Fonterra. Fonterra Pacific. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
- Anchor Food Professionals. "Cheese Products". Anchor Foods. Fonterra Co-operative Group. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
External links
 Media related to Camembert (cheese) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Camembert (cheese) at Wikimedia Commons