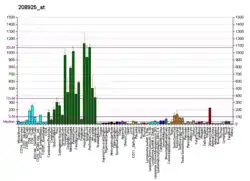
CLDND1
Claudin domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLDND1 gene.[5]
| CLDND1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CLDND1, C3orf4, GENX-3745, claudin domain containing 1, Z38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 2447860 HomoloGene: 10534 GeneCards: CLDND1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000080822 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022744 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: CLDND1 claudin domain containing 1".
External links
- Human CLDND1 genome location and CLDND1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Liu Y, Sun W, Zhang K, et al. (2007). "Identification of genes differentially expressed in human primary lung squamous cell carcinoma". Lung Cancer. 56 (3): 307–17. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.01.016. PMID 17316888.
- Otsuki T, Ota T, Nishikawa T, et al. (2007). "Signal sequence and keyword trap in silico for selection of full-length human cDNAs encoding secretion or membrane proteins from oligo-capped cDNA libraries". DNA Res. 12 (2): 117–26. doi:10.1093/dnares/12.2.117. PMID 16303743.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, et al. (2003). "The Secreted Protein Discovery Initiative (SPDI), a Large-Scale Effort to Identify Novel Human Secreted and Transmembrane Proteins: A Bioinformatics Assessment". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697. PMID 12975309.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Fayein NA, Stankoff B, Auffray C, Devignes MD (2002). "Characterization of tissue expression and full-length coding sequence of a novel human gene mapping at 3q12.1 and transcribed in oligodendrocytes". Gene. 289 (1–2): 119–29. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00507-3. PMID 12036590.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and Functional Analysis of cDNAs with Open Reading Frames for 300 Previously Undefined Genes Expressed in CD34+ Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Piétu G, Mariage-Samson R, Fayein NA, et al. (1999). "The Genexpress IMAGE Knowledge Base of the Human Brain Transcriptome: A Prototype Integrated Resource for Functional and Computational Genomics". Genome Res. 9 (2): 195–209. doi:10.1101/gr.9.2.195. PMC 310711. PMID 10022985.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.