C3orf62
Chromosome 3 Open Reading Frame 62 (C3orf62), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C3orf62 gene. C3orf62 is a glycine depleted protein relative to the amount of glycine in proteins in the rest of the genome.[5] C3orf62 has a KKXX-like motif and is predicted to be localized in the nucleus.[6] Expression of C3orf62 remains highest in whole blood.[7]
| C3orf62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | C3orf62, chromosome 3 open reading frame 62, MAPS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 2148248 HomoloGene: 14230 GeneCards: C3orf62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C3orf62 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | C3orf62 | ||||||
| Alt. names | CC062, FLJ43654 | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 375341 | ||||||
| HGNC | 24771 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_198562.21 | ||||||
| UniProt | Q6ZUJ4 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 3 p21.31{{{LocusSupplementaryData}}} | ||||||
| |||||||
Gene
Locus
C3orf62 is mapped to the reverse strand of chromosome 3 at 3p21.31 and spans 9.313 bases.[8] C3orf62 starts at 49,268,597 base pairs from the terminus of the short arm (pter) and ending at 49,277,909 base pairs pter. This gene is known to have 3 exons, 4 transcripts, and 37 orthologues.[9][7][10][11][12]
Gene neighborhood
C3orf62 is flanked by Ubiquitin Specific Protease 4 (USP4) and Coil-Coiled Domain Containing 36 (CCDC36).
Protein
Primary sequence
C3orf62 human protein (Q6ZUJ4) is 267 amino acids long, and has a molecular mass of 30,194 Daltons.[9] The isoelectric point of C3orf62 is roughly 5.2. The unmodified C3orf62 protein is a “glycine depleted protein” relative to amounts of glycine in proteins in the rest of the genome.[5] It appears that glycine is evenly distributed throughout the C3orf62 sequence with no preference of areas to cluster in. Before post-translational modifications, C3orf62 is an acidic protein. No charge clusters are present in C3orf62, and no specific spacing of cysteine is found. The isoelectric point of C3orf62 is 5.211000.[14]
| Name | Ensembl Transcript ID[11][7] | Base Pairs | Protein | Biotype | CCDS | Uniprot | Refseq | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3orf62-001 | ENST00000343010.7 | 4235 | 267aa | Protein encoding | CCDS2792 | Q6ZUJ4 | NM_198562, NP_940964 | |
| C3orf62-004 | ENST00000436325.1 | 581 | 190aa | Protein encoding | - | C9JW57 | - | |
| C3orf62-003 | ENST00000424960.1 | 602 | 98aa | Nonsense mediated decay | - | H7BZX3 | - | |
| C3orf62-002 | ENST00000479673.1 | 3330 | No protein | Retained intron | - | - | - |
Domains and motifs
There are no known transmembrane domains for C3orf62.[13] C3orf62 has a KKXX-like motif in the C-terminus meaning C3orf62 may be responsible for retrieval of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane proteins from the Golgi apparatus.[15]
Secondary structure
Roughly 7 alpha helices are predicted for C3orf62 through Pele Protein Structure Protein Prediction and strengthened through orthologous secondary structure predictions by Ali2D.[13][16]
Subcellular localization
C3orf62 is predicted to be localized in the nucleus.[6] The k-nearest neighbors algorithm predicts C3orf62 to be classified as follows: k=9/23; 69.6% nuclear, 13.0% mitochondrial, 13.0% cytoskeletal, 4.3% cytoplasmic.[6]
Expression
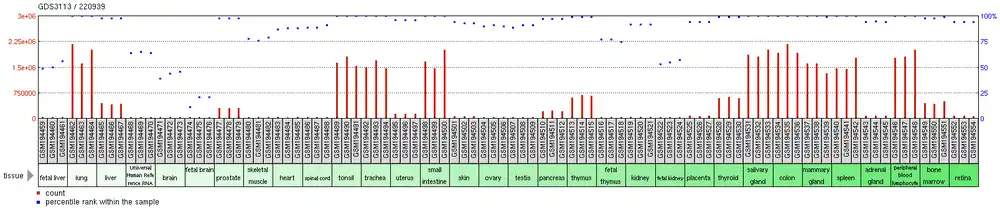
C3orf62 is expressed in more than 30 different tissues; highest expression is in whole blood.[10][7][9] Specifically, highest expression of C3orf62 is in the following tissues: lung, tonsil, trachea, small intestine, mammary gland, and salivary gland. Through analysis of various microarray studies, C3orf62 is found to have consistently high expression compared to other genes tested in the datasets.[17] C3orf62 has low expression in brain tissues.
Post-transcriptional modifications
C3orf62 possess two post-translational modifications, both are phosphorylation sites with locations at amino acid 210 and 224.[9] A natural variant is found at amino acid 110 (Glutamic acid (E)--> Lysine K).[12][11]
It appears as though C3orf62 may have a YinOYang site at residue 115, meaning that this Threonine residue is predicted to be O-GlycNAcylated as well as phosphorylated. This site may be reversibly and dynamically modified by O-GlcNAc or Phosphate groups at different times in the cell.[18]
Transcript variants
Transcription of C3orf62 produces 5 alternatively spliced variants and 1 unspliced form. Of the four splice variants, two of them are protein coding, one is nonsense meditated decay, and one is a retained intron.[10] QIAGEN denotes the following as transcription factor binding sites in the C3orf62 promoter: TFCP2, Pax-6, p53, MyoD, YY1, Ik-2, AREB6, IRF-7A3.[7]
Function
Function of C3orf62 is not currently understood by the scientific community.
Interactions
Upwards of 12 interacting proteins have been predicted for C3orf62.[20][21][22] Interacting proteins with the strongest confidence to interact with C3orf62 include: HAUS augmin-like complex subunit 1 (HAUS-1), Inhibitor of growth protein 5 (ING5), Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 9 (TXNDC9), and MORF4-family associated proteins (MORF4L1, MFRAP1).
Chemicals known to interact with C3orf62 include the following: Aflatoxin B1, Hydralazine, Valproic acid, and Decitabine.[10]
Clinical significance
Interstitial deletions of chromosome 3 are rare, and only a few patients with a microdeletion of 3p21.31 have been reported to date. Characteristic clinical features found in patients with a microdeletion of 3p21.31 include developmental delay and distinctive facial features (including arched eyebrows, hypertelorism, epicanthus, and micrognathia).[23][24][25]
In the gene region, NCBI SNP identified 1,326 SNPS on the reverse minus strand of C3orf62.[26] In the coding region, NCBI SNP identified 147 common SNPs.
Homology
Paralogs
There are no known paralogs of C3orf62.[27]
Orthologs
The ortholog space of C3orf62 is fairly narrow, with the majority of orthologs found in mammals.[27] A small fraction of orthologs have also been found in the following classes: Reptila, Sarcopterygii, and Actinoptergii.
The groupings of nearly all Mammalia ortholog sequences of C3orf62 are as follows: E-value: 2e-94 to 1e-169; similarity 56-84%. Mammals in this group consist largely of primates but also include the following orders: Perissodactyla, Rodentia, Carnivora, Proboscidea, Cetartiodactyla, Cingulata, Artiodactyla, Eulipotyphla, Diselphimorphia, and Afrosoricida.[27]
More distantly related ortholog sequences of C3orf62 include organisms from classes Reptilia, Sarcopterygii, and Actinopterygii ranging from an E-value of 8e-10 to 3e-59 with similarity of 24-39%.[27] Organisms in this grouping consist of Testudines, Coelacanthiformes, Squamata, and Osteoglossiformes orders. No ortholog sequences of C3orf62 were found for the following life forms: Bacteria, archaea, protist, plant, fungus, trichoplax, invertebrate, amphibian, or bird.
| Genus and Species | Common Name | Class | Accession | Percent Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human | Mammalia | NP_940964 | 100 |
| Microcebus murinus | Grey Mouse Lemur | Mammalia | XP_012626718 | 88 |
| Propithecus coquereli | Coquerel's sifaka (lemur) | Mammalia | XP_012510880 | 86.9 |
| Equus caballus | Horse | Mammalia | NP_001295877 | 84.3 |
| Loxodonta Africana | African elephant | Mammalia | XP_003409711 | 83.2 |
| Castor Canadensis | North American Beaver | Mammalia | XP_020037316 | 81.6 |
| Otolemur garnettii | Garnett's Greater Galago | Mammalia | XP_003800633 | 81.6 |
| Camelus bactrianus | Bactrian camel | Mammalia | XP_010967491.1 | 78.3 |
| Ailuropoda melanoleuca | Giant Panda | Mammalia | XP_019656626 | 77.7 |
| Canis lupus familiaris | Dog | Mammalia | XP_003432924 | 77.2 |
| Vicugna pacos | Alpaca | Mammalia | XP_006196356 | 77.2 |
| Condylura cristata | Star-nosed mole | Mammalia | XP_012575760 | 76.8 |
| Felis catus | Cat | Mammalia | XP_003982269 | 75.1 |
| Pteropus vampyrus | Large flying fox | Mammalia | XP_011373720 | 73.3 |
| Pantholops hodgsonii | Tibetan antelope | Mammalia | XP_005969318 | 72.6 |
| Ictidomys tridecemlineatus | Thirteen lines ground squirrel | Mammalia | XP_005326967 | 71 |
| Sorex araneus | Common Shrew | Mammalia | XP_012789682 | 69.5 |
| Monodelphis domestica | Gray short-tailed opossum | Mammalia | XP_001367907 | 65.4 |
| Echinops telfairi | Lesser Hedgehog Tenrec | Mammalia | XP_004715283 | 63.7 |
| Orcinus orca | Killer whale | Mammalia | XP_004283985 | 61.2 |
| Dasypus novemcinctus | Nine banded armadillo | Mammalia | XP_004451950 | 58.2 |
| Dipodomys ordii | Ord's Kangaroo Rat | Mammalia | XP_012883511 | 56.3 |
| Myotis lucifugus | Little Brown Myotis | Mammalia | XP_006107033 | 39.3 |
| Pelodiscus sinensis | Chinese softshell turtle | Reptillia | XP_014426235 | 38.5 |
| Chelonia mydas | Green Sea Turtle | Reptillia | XP_007061837 | 37.1 |
| Latimeria chalumnae | West Indian Ocean coelacanth (fish) | Sarcopterygii | XP_005992740 | 35.3 |
| Anolis carolinensis | Green anole (lizard) | Reptillia | XP_008103227 | 33.1 |
| Gekko japonicus | Japanese Gecko | Reptillia | XP_015262861 | 30.1 |
Phylogeny
The most distant ortholog of C3orf62 are species of fish and amphibians. Orthologs of C3orf62 are not seen in birds, invertebrates, or bacteria.[27]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000188315 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032611 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "SAPS". SDSC Biology Workbench. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- "C3orf62 Homo sapiens". PSORT WWW Server.
- "Homo sapiens C3orf62". GeneCards. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- "Homo sapiens C3orf62". NCBI Nucleotide. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- "Homo sapiens C3orf62". NCBI Gene. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- "Humans 2010-C3orf62". Aceview. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- "C3orf62". UniProtKB.
- "C3orf62". Ensembl. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- "Human Gene C3orf62". UCSC. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- "PI". SDSC Biology Workbench.
- "C3orf62". PSORT WWW Server. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "C3orf62". Ali2D. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "C3orf62 GEO Profiles". NCBI GEO. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- "C3orf62". YingOYang. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "C3orf62". Genomatix. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "C3orf62". STRING Interaction Network. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "C3orf62". BioGRID. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "C3orf62". InAct. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- Haldeman-Englert CR, Gai X, Perin JC, Ciano M, Halbach SS, Geiger EA, McDonald-McGinn DM, Hakonarson H, Zackai EH, Shaikh TH (13 Dec 2008). "A 3.1-Mb microdeletion of 3p21.31 associated with cortical blindness, cleft lip, CNS abnormalities, and developmental delay". European Journal of Medical Genetics. 52 (4): 265–8. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2008.11.005. PMC 4391973. PMID 19100872.
- Eto K, Sakai N, Shimada S, Shioda M, Ishigaki K, Hamada Y, Shinpo M, Azuma J, Tominaga K, Shimojima K, Ozono K, Osawa M, Yamamoto T (December 2013). "Microdeletions of 3p21.31 characterized by developmental delay, distinctive features, elevated serum creatine kinase levels, and white matter involvement". American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A. 161A (12): 3049–56. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.36156. PMID 24039031. S2CID 272908.
- Lovrecic L, Bertok S, Žerjav Tanšek M (May 2016). "A New Case of an Extremely Rare 3p21.31 Interstitial Deletion". Molecular Syndromology. 7 (2): 93–8. doi:10.1159/000445227. PMC 4906427. PMID 27385966.
- "C3orf62". NCBI SNP.
- "C3orf62". NCBI BLAST. Retrieved 7 May 2017.