North Borneo Chartered Company
The North Borneo Chartered Company (NBCC), also known as the British North Borneo Company (BNBC) was a British chartered company formed on 1 November 1881 to administer and exploit the resources of North Borneo (present-day Sabah in Malaysia). The territory became a protectorate of the British Empire in 1888 but the company remained involved with the territory until 1946, when administration was fully assumed by the Crown colony government.[1][2]

The company also temporarily administered the island of Labuan in 1890 before it became part of the Straits Settlements.[3][4][5] The company motto was Pergo et Perago, which means "I persevere and I achieve" in Latin. Its founder and first chairman was Alfred Dent.[6][7]
History
Foundation

The company was founded along similar lines as the British East India Company. German businessman and diplomat Baron von Overbeck, along with the heads of a British trading company in Shanghai and London, Alfred Dent and Edward Dent, together met with the thalassocratic rulers of the northern Borneo area to obtain a concession for their colonial interests.[8] The governor of Labuan, a British colonial island off Brunei, accompanied the negotiations. On 29 December 1877, they met Abdul Momin, Sultan of Brunei. The Sultan agreed to make the concession for 15,000 Spanish dollars. However, since it turned out that the Sultan of Brunei had already ceded some areas to the Sultan of Sulu, further negotiations were needed. With the assistance of William Clark Cowie, a Scottish adventurer and friend of Sultan Jamal-ul Azam of Sulu, the Sultan signed a concession treaty on 22 January 1878 and received 5,000 Spanish dollars.[9][10]
Following the successful concessions, Overbeck and the Dent brothers became the rulers of an area in northern Borneo. Overbeck withdrew in 1879 after failing to attract the interest of his country, leaving Alfred Dent to manage the territory. Dent then planned to register a company to represent the British but since a considerably delay seemed likely, he decided to found a provisional company first. In 1881, the British North Borneo Provisional Association Limited was founded with registered capital of £300,000. The directors were Dent himself together with Rutherford Alcock, Richard Biddulph Martin, Admiral Richard Mayne and William Henry Read. The charter contract for a company with a capital of two million pounds was sealed on 1 November 1881.[11]
The provisional company was thus dissolved and the following year, a chartered company was established with a first settlement on Gaya Island.[12][13] The settlement however was burnt down during a raid by a local leader named Mat Salleh and was never re-established. Due to such resistance, establishing law and order as well as recruiting Sikh policemen from northern India became one of the company's earlies priorities, along with expanding trade; instituting a government, courts, and penal system; building a railway line from Jesselton to Tenom; and encouraging the harvesting and barter trade of local crops, as well as establishment of plantations.[14][15] The company also faced some resistance to its economic modernisations and tax policies.[16]
Dissolution
No other state in the British Commonwealth was as devastated by the Second World War as North Borneo. By the end of the war, it was already foreseeable that the company would be unable to finance remediation for the devastation to land and infrastructure.[17] The company therefore waived the further use of their charter and gave British North Borneo to the British Colonial Office. With the signing of an agreement on 26 June 1946, the company officially dissolved. From 15 July 1946 until the formation of Malaysia on 16 September 1963, North Borneo was a Crown colony. The agreement with the British government included a £860,000 immediate cash settlement that allowed the company to settle outstanding financial claims. The government's offer to repay all other claims by paying 2.2 million pounds had already been rejected by the company. For the negotiation of further financial compensation, the British government appointed Lord Uthwatt as an independent arbitrator.[18][19] In March 1949, Uthwatt announced the result of his investigations: £1,400,000 should be awarded to the company as compensation; any claims related to war damage would not be included. The news triggered a bitter disappointment among shareholders. In just overnight, the value of the company share fell from 17s to 9s 6p.[20]
Administration

With the founding of the company, the administrative divisions of North Borneo introduced by Overbeck were maintained by the establishment of the West Coast Residency and the East Coast Residency. The seat of the two residents was in Sandakan, where the governor was based. Each residency, in turn, was divided into several provinces managed by a district officer.[note 1][21] Over time, the number of residencies increased to five: Tawau Residency (also known as East Coast Residency), Sandakan Residency, West Coast Residency, Kudat Residency, and Interior Residency. The provinces were initially named after the members of the board: Alcock, Cunlife, Dewhurst, Keppel, Dent, Martin, Elphinstone, Myburgh and Mayne. The senior residents occupied Sandakan and the West Coast, while the other three residents with the second class residencies occupied Interior, East Coast and Kudat. The residents of Sandakan and West Coast were members of the Legislative Council, the Legislative Assembly of the Company.[22]
The election of Cowie to the board of directors in 1894 marked the beginning of a major change in the style of administration: Before, North Borneo was governed by the company, and the governors were fully empowered and fully responsible. But since Cowie took over, he mostly pulled strings from London. Instead of the development of North Borneo, the satisfaction of the shareholders was in the foreground. Alfred Dent, who fiercely opposed Cowie's costly and money-wasting ideas, finally resigned and withdrew from the company.[23]
Under Neill Malcolm, the administration was ordered to strictly supervise expenditure.[24] Several governors reduced the number of district officers by eliminating the posts in Ranau, Pensiangan, Tenom, Sipitang, Penampang, Tuaran, Langkon, Lamag, Beluran and Semporna. Douglas James Jardine, who become the governor in 1934, completed the process by merging the Tawau Residency with the Sandakan Residency on the one hand and the Interior Residency with the West Coast on the other hand. He also removed the District Officer in Papar.[25][26]
Municipal administration was governed by the Village Ordinance of 1891. This ordinance fundamentally changed the status of the chiefs, the traditional indigenous tribal leaders. Following its implementation, the company only accepted those chiefs who had appointed them as community leaders. Other chieftains, who had played an important role for generations, were either shut down or branded as criminals or troublemakers. Disrespect for these traditional leaders contributed to the spirit of local resistance led by tribal group such as Mat Salleh and Ontoros Antanum.[16][27][28]
Tasks
The company had two responsibilities, namely:[29]
- Economic development through the exploitation of natural resources of the area. The company was authorised to use the area for agriculture, to settle it, to promote immigration, to mine and to cut wood. An employee of the company and later plantation owner in North Borneo, Owen Rutter, openly named the purpose of "producing dividends".
- Due to the experience of the decline of the British East India Company, a passage was written to protect the rights of the residents. The company was legally responsible for protecting the customs and rights of its residents, but in practice it had to pay dividends, which often limited those rights.
The first governor of North Borneo, William Hood Treacher, devoted himself especially to the elimination of slavery. However, the land laws issued by him in no way respected the traditional land rights of the inhabitants. The second governor, Charles Vandeleur Creagh, in 1888, issued several proclamations that largely secured foreigners' access to land. A board of directors in London determined the tasks of the company over the governors. Locally, directors over-ruled the governor's instructions. The company established a state power, issued laws (proclamations), recruited Sikh policemen from northern India.[14] Courts were set up to enforce the laws. Furthering the economic exploitation of the area was the construction of a railway line (North Borneo Railway) from Jesselton to Weston and Melalap, the promotion of trade and the establishment of plantations.[15][29] Effective from 1 March 1883, the periodical North Borneo Herald and Official Gazette was published to disseminate the decisions of the Court of Directors, both within the administrative units of North Borneo, and the company's shareholders and investors.
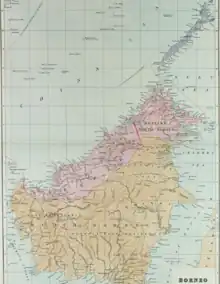
Territory
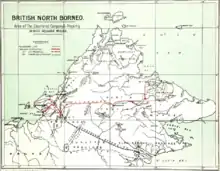
A major contribution to the consolidation of the administrative area was made by William Hood Treacher. In tough negotiations with the White Rajahs, he managed to bring territories to the company that were not included in the original leases. These includes Pengalat (1883), Klias Peninsular (1884), Mantanani (1885), Padas (1889) and the area of Sipitang, Bongawan to Tuaran (1889). From 1889, the island of Labuan was also part of the company administrative territory.[5]
Although the Netherlands had already installed a trading post in Borneo shortly after the founding of the Dutch East India Company, there were no noteworthy activities by the Dutch on the east coast of northern Borneo. This changed in 1846 when the Dutch signed a contract with the Sultan of Bulungan, who assured the Dutch control of the area. At the instigation of the Dutch, the sultan married his son in 1867 with the daughter of the Sultan of Tarakan, whereby the Dutch sphere of influence finally reached the region around Tawau. The north of the Dutch area which overlapped with an area that was claimed by the Sultanate of Sulu for themselves. A conflict with the British was therefore inevitable when in 1878 the Sultan of Sulu placed the southern boundary of his land for cession to Overbeck on the Sibuku River. In settling the border disputes, the company negotiated with the Dutch from the 1880s onwards to define the boundary between the area granted by the Sultan of Sulu and the area claimed by the Dutch on the basis of the treaty with the Sultan of Bulungan. On 20 January 1891, they finally agreed on a line along 4°10' north latitude – which corresponded to a central division of the island of Sebatik.[note 2][30]
On 5 January 1905, the company territory of Lawas – a controversial border area of the province of Clark was relinquished to the neighbouring Sarawak and in exchange for “certain coal fields at the Brunei Bay”.[31][32][33]
List of presidents
The head of the company was the chairman of the board of directors, since 1910 officially named as President:
| Chairman of the British North Borneo Chartered Company | |
| 1881–1882 | Alfred Dent |
| 1882–1893 | Rutherford Alcock |
| 1893–1903 | Richard Biddulph Martin |
| 1903–1909 | Charles Jessel |
| 1909 – 14 September 1910 | William Clark Cowie |
| Presidents of the British North Borneo Chartered Company | |
| 1910–1926 | Joseph West Ridgeway |
| 3 February 1926 – 15 July 1946 | Neill Malcolm |
Notes
- The original position was initially Magistrates-in-charge.
- The final contractual stipulation of this border was not confirmed until 1912 by the Joint Boundary Commission and was parried on 17 February 1913 by Dutch and British negotiators.
Footnotes
- The National Archives 1945, pp. 2.
- Encyclopædia Britannica 1992, pp. 278.
- Renton et al. 1908.
- United States. Hydrographic Office 1917.
- Madden, Fieldhouse & Darwin 1985, pp. 555.
- Great Britain. Foreign Office 1888, pp. 238.
- Treacher 1891, pp. 165.
- Tarling 2003, pp. 63.
- Rutter 1922, pp. 119.
- Lim 2008, pp. 17.
- Treacher 1891, pp. 101–102.
- British North Borneo 1881.
- Hansard Parliament 1882.
- Hansard Parliament 1892.
- Dickinson 2000.
- Fernandez 1999.
- Hansard Parliament 1947.
- The National Archives 1946.
- Tregonning 1965, pp. 222–223.
- Sunday Tribune 1949.
- Tregonning 1965, pp. 51.
- Rutter 1922, pp. 157.
- Tregonning 1965, pp. 53.
- Tarling 2003, pp. 214.
- Osman 1989.
- Danny 2009.
- Fernandez 2001.
- Sabah State Archives 2007, pp. 5.
- Doolittle 2011.
- Trost 1995, pp. 6.
- Ledesma, Lewis & Savage 2003, pp. 723.
- Runciman 2011, pp. 197.
- Lawas District Council 2017.
References
- British North Borneo (1881). Charter granted to the British North Borneo Company (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2017.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - Hansard Parliament (1882). "British North Borneo Company (Charter) – Observations". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). Archived from the original on 4 November 2017.
- Great Britain. Foreign Office (1888). British and Foreign State Papers. H.M. Stationery Office.
- Treacher, W. H (1891). "British Borneo: sketches of Brunai, Sarawak, Labuan, and North Borneo". University of California Libraries. Singapore, Govt. print. dept. p. 190.
- Hansard Parliament (1892). "North Borneo". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). Archived from the original on 4 November 2017.
- Renton, Alexander Wood; Robertson, Maxwell Anderson; Pollock, Frederick; Bowstead, William (1908). Encyclopædia of the laws of England with forms and precedents by the most eminent legal authorities. Sweet & Maxwell.
- United States. Hydrographic Office (1917). Asiatic Pilot: The coasts of Sumatra and the adjacent straits and islands. Hydrographic office under the authority of the secretary of the navy.
- Rutter, Owen (1922). "British North Borneo - An Account of its History, Resources and Native Tribes". Cornell University Libraries. Constable & Company Ltd, London. p. 157.
- The National Archives (1945). "Policy in Regard to Malaya and Borneo" (PDF). Memorandum by the Secretary of State for the Colonies. The National Archives. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2017.
- The National Archives (1946). "Chartered Company of North Borneo. Proposals that Cyril Radcliffe should be appointed Arbitrator in connection with transfer of company to H.M. Government Proposal that Lord Uthwatt be appointed Arbitrator". The National Archives.
- Hansard Parliament (1947). "British Firms, Borneo (Taxation)". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). Archived from the original on 4 November 2017.
- Sunday Tribune (1949). "Award For Br. North Borneo Co". National Library Board.
- Tregonning, K. G. (1965). A History Of Modern Sabah (North Borneo 1881–1963). University of Malaya Press.
- Galbraith, John S. (May 1965). "The Chartering of the British North Borneo Company". Journal of British Studies. Cambridge University Press for The North American Conference on British Studies. 4 (2): 102–126. doi:10.1086/385502. JSTOR 175148.
- Madden, A. F.; Fieldhouse, David Kenneth; Darwin, John (1985). Select Documents on the Constitutional History of the British Empire and Commonwealth: "The Empire of the Bretaignes," 1175-1688. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-23897-0.
- Osman, Sabihah (1989). "The Role of Governor D. J. Jardine in Improving the Welfare of the Indigenous People of Sabah, 1934-37". Journal of Southeast Asian Studies. Cambridge University Press on behalf of Department of History, National University of Singapore, JSTOR. 20 (2): 192–215. doi:10.1017/S0022463400018099. JSTOR 20071080.
- Encyclopædia Britannica (1992). "Sabah" in The New Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 10. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. p. 278.
- Trost, R. Haller (1995). The Territorial Dispute Between Indonesia and Malaysia Over Pulau Sipadan and Pulau Ligitan in the Celebes Sea: A Study in International Law. IBRU. ISBN 978-1-897643-20-4.
- Fernandez, Callistus (1999). "Contesting Colonial Discourse: Rewriting Murut History of Resistance in British North Borneo from 1881 to 1915" (PDF). Faculty of Development Science, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. Universiti Sains Malaysia. pp. 81–103. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2017.
- Dickinson, Rob (2000). "The North Borneo Railway Project". The International Steam Pages. Archived from the original on 28 March 2013.
- Fernandez, Callistus (2001). "The Legend by Sue Harris: A Critique of the Rundum Rebellion and a Counter Argument of the Rebellion" (PDF). Department of Sociology, National University of Singapore. Universiti Sains Malaysia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 June 2016.
- Tarling, Nicholas (2003). Imperialism in Southeast Asia. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-57082-9.
- Ledesma, Charles de; Lewis, Mark; Savage, Pauline (2003). Malaysia, Singapore and Brunei. Rough Guides. ISBN 978-1-84353-094-7.
- Sabah State Archives (2007). Datu Paduka Mat Salleh – Hero of Sabah (1894–1900). Sabah State Archives.
- Lim, Regina (2008). Federal-state Relations in Sabah, Malaysia: The Berjaya Administration, 1976–85. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. ISBN 978-981-230-812-2.
- Danny, Wong Tze-Ken (2009). "Woolley and the Codification of Native Customs in Sabah" (PDF). University of Malaya. New Zealand Journal of Asian Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2017.
- Doolittle, Amity A. (2011). Property and Politics in Sabah, Malaysia: Native Struggles Over Land Rights. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0-295-80116-2.
- Runciman, Steven (2011). The White Rajah: A History of Sarawak from 1841 to 1946. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-12899-5.
- Lawas District Council (2017). "Background" (in Malay and English). Sarawak State Government.
Further reading
- British North Borneo Chartered Company (1878). "British North Borneo company charter". Cornell University Library. [S.l. : s.n. p. 32.
External links
![]() Media related to North Borneo Chartered Company at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to North Borneo Chartered Company at Wikimedia Commons
- Documents and clippings about North Borneo Chartered Company in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
- The papers of the British North Borneo Company are held by SOAS Special Collections