Blackhand Gorge State Nature Preserve
The Blackhand Gorge State Nature Preserve is a 4-mile-long (6.4 km) sandstone formation through which the Licking River flows in Licking County, Ohio, United States. Located 12 miles (19 km) east of Newark near the tiny town of Toboso, 957 acres (387 ha) along the gorge were designated an Ohio Nature Preserve in 1975. The gorge is a capsule of Ohio transportation history, having hosted canal boats, steam railroads, electric interurbans, and automobiles through the years. It is named for the black hand petroglyph that was found on the cliff face by the first settlers to the area. Black Hand Sandstone is a resistant rock that also forms the backbone of the Hocking Hills region.
| Blackhand Gorge State Nature Preserve | |
|---|---|
 | |
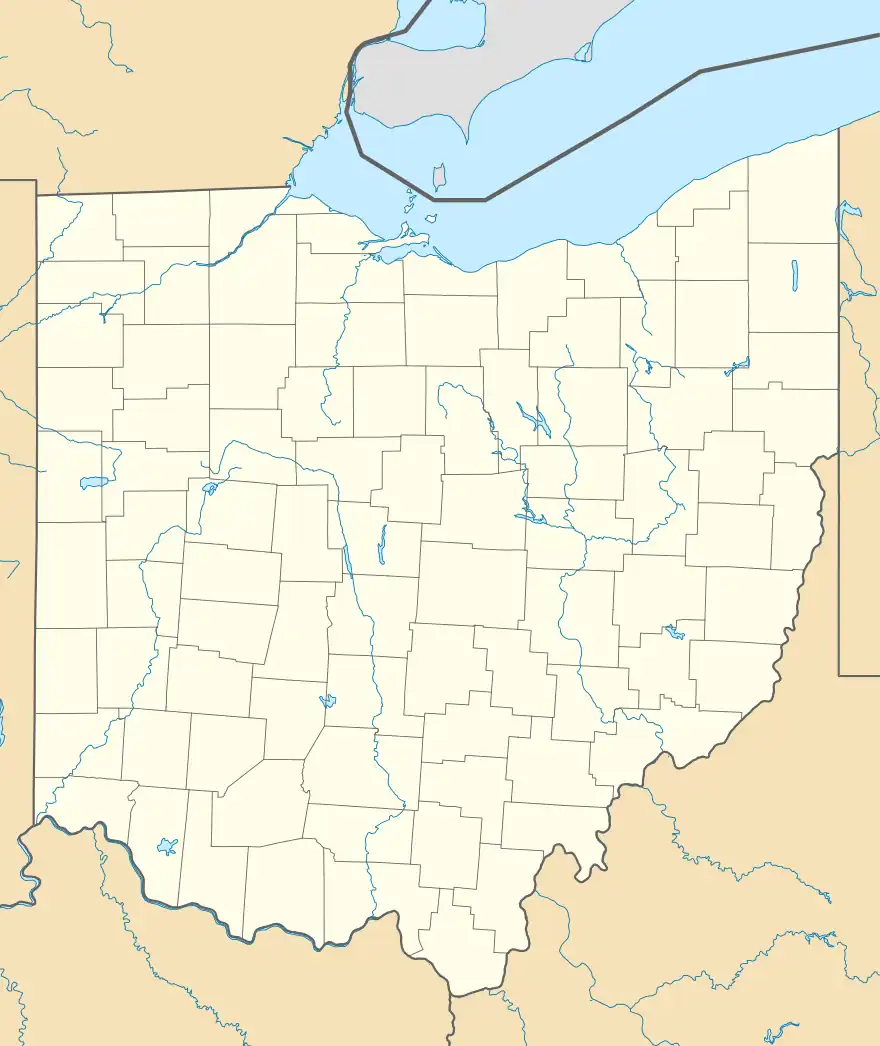  | |
| Location | Licking County, Ohio |
| Nearest city | Newark, Ohio |
| Coordinates | 40.056°N 82.24847°W |
| Area | 957 acres (387 ha) |
| Established | 1975 |
| Governing body | Ohio Department of Natural Resources |
| naturepreserves | |
History
From 13,000 BC to 400 AD the Early Native American Indians (including Hopewell Indians) lived in the area and visited the gorge. Beginning in the early 19th century, Anglo-European settlers used it as a transportation route through the hilly east-central Ohio landscape.
Legend of the Black Hand
One origin legend describes a contest set up between two suitors. The loser amputated his own hand in shame and threw it off one of the gorge's cliffs (possibly above the current location of the railroad tunnel), creating a hand-shaped mark on the rock.
For complete review of the Blackhand Gorge, including the legend of the Black Hand, see Blackhand Gorge: A Journey Through Time by Aaron Keirns. It was first published in 1995 by Little River Publishing.
The Black Hand
The Blackhand Gorge was named after the Black Hand, a prehistoric petroglyph in the shape of a black hand with spread fingers and part of a wrist. One elongated finger supposedly pointed towards a nearby Indian mound. It is thought that the symbol meant that all tribes passing through the gorge on their way to the flint pits a few miles south must pass through in peace. The rock was destroyed in 1828 during the construction of the Ohio and Erie Canal. Other petroglyphs survived until 1890, many recorded by Dr. James Salisbury and his brother Charles, of Newark, who deposited their tracings and notes with the American Antiquarian Society in Massachusetts. Blasting for the electric interurban railway in 1890 removed the last traces of almost all prehistoric stone carving.
The Legend Of The Black Hand Gorge
Many legends have been left by the Native American Indians. One of the most beautiful is Ahyoma, the daughter of Chief Pawcongah and the "Black Hand".
The Indians needed something sharp on the tips of their arrows to kill their prey and flint was chosen for this purpose. A ridge between Zanesville and Newark abounded with this natural resource. Indian tribes from all over the area now known as Ohio, would come to this spot known as Flint Ridge.
The legends say that the "Great Father" called the tribes together on a council rock not far from Flint Ridge. The chiefs all sat in a big circle and the "Great Father" told them when they were in the pits, no more blood could be shed. This area known as Flint Ridge, would be sacred ground.
Many moons passed and the tribes heeded this warning. They shared this valuable resource, known as flint, and no blood was shed.
The great chief Pawcongah, had a beautiful daughter named Ahyoma. Many braves wanted her hand in marriage. Her father said that the one that shall bring forth the greatest amount of scalps, would be given his daughter's hand in marriage.
Many braves went into battle, but only two returned to claim the young girl's hand for his bride.
The first Waconsta, who took from his belt his trophies and laid them one at a time at the feet of the chief.
Then came the second brave Lahkopis who was very dear to the heart of Ahyoma. Waconsta, had the most scalps though, and would be the one to marry the chief's daughter the very next day. Later that night, the daughter decided to leave with the other brave Lahkopis, her true love. They decided that if they could reach the sacred ground at Flint Ridge, that they would be safe. No blood was permitted to be shed at that spot.
Waconsta pursued them, forgetting the curse that would be upon any Indian who killed another on the sacred ground. As the two lovers stood on the high ridge, Waconsta raised his tomahawk to strike. Lahkopis, the true love of the girl, raised his hand in defense with his own tomahawk and cut off the hand of his attacker with one swoop.
The Indian maiden and her lover fell into the raging Licking River during their struggle. The hand of Waconsta, fell with them and clung to the side of the cliff. The hand turned black and grew in size. It remained as a warning to all tribes. Never again would blood be spilled at the arrow pits of Flint Ridge.
The canal came through this area in 1828 and the part of the rock that contained the remains of the hand, was blasted away to make room for the towpath.
The region is now known as the "Black Hand Gorge".
The Ohio and Erie Canal (1825)
On July 4, 1825, Governors Clinton of New York and Morrow of Ohio threw the first shovels-full of dirt at the Licking Summit near Newark, Ohio on the Ohio and Erie Canal project. Due to lack of transportation, Ohio farmers were essentially unable to sell their goods at any price, and Ohio was mired in a cash-poor depression. The canal would connect farmers to Lake Erie and the Ohio River.
The specifications for the canal required a width of 40 feet (12 m) at the top and 26 feet (7.9 m) at the bottom. The depth was to never be less than 4 feet (1.2 m). From the Licking Summit the canal proceeded east along the north side of the Licking River, crossed Rocky Fork Creek on an aqueduct. An inlet lock then connected the canal to the Licking River, which due to the sandstone formations, was the only way to get through the Blackhand Gorge. A dam was built on the Licking River at Toboso to provide a constant pool in the gorge. An outlet lock near the dam allowed the canal boats to exit the Licking River and continue on their way.
In some places the sides of the gorge had to be blasted away and a stone pathway constructed to act as a towpath.
Ohio's canal era peaked in the 1850s and then began a decline into the early 20th century. The Great Flood of 1913 damaged the infrastructure to the point where the canal was no longer navigable.
The Central Ohio Railroad (1850)
The first rails were laid in Blackhand Gorge in 1850 by the Central Ohio Railroad. The tracks hugged the river's edge from Claylick to Toboso. It took one year to carve through a solid mass of sandstone 64 feet (20 m) high and 700 feet (210 m) long producing "The Deep Cut". Trains began running in 1851, and in 1865 the Central Ohio Railroad became part of the Baltimore and Ohio railroad. In 1958 the construction of Dillon Dam and its resulting reservoir on the Licking River required that the tracks through the gorge be abandoned for a new route.
The Ohio Electric Interurban (1890)
In October, 1890 an electric interurban was running from Newark to Granville. The line wasn't opened to Zanesville until 1903 due to difficulties cutting a pathway through the gorge. An interurban tunnel 19.5 feet (5.9 m) high and 327 feet (100 m) long was blasted through solid rock to complete the job. The interurban ran on the opposite side of the Licking River from the B&O Railroad.
The interurban was short-lived due to the rising popularity of the automobile. The last Ohio Electric Interurban car ran through the gorge on February 15, 1929.
Dillon Dam (1961)
Construction of Dillon Dam began in June 1946, but work was halted due to lack of funds, and then a shortage of materials due to the outbreak of the Korean War. Construction on the dam resumed in 1958 and it was completed in June 1961. The dam protects the Muskingum Valley, including the cities of Zanesville, McConnelsville, and Marietta.
Unfortunately, the reservoir formed by the dam completely submerged Claylick and required that most of the town of Toboso be torn down. Opposition to the project was fierce for that reason, but the benefits of the dam served a wide constituency and construction was not prevented.
References
- Keirns, Aaron J., Black Hand Gorge, A Journey Through Time, Little River Publishing, Howard, Ohio, 1995, ISBN 0-9647800-0-3
External links
- Blackhand Gorge: A Journey Through Time. The resource for BHG information
- Ohio Department of Natural Resources Division of Natural Areas and Preserves Black Hand Gorge website
- Army Corps of Engineers Official Dillon Lake website
- Ohio Historical Society Black Hand Gorge photo
- A hike through Black Hand Gorge
- Deposits of Glass Sand at Toboso, Ohio