Berlioz (crater)
Berlioz is a crater on Mercury, located near the north pole. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2013. It is named for the French composer Hector Berlioz.[1]
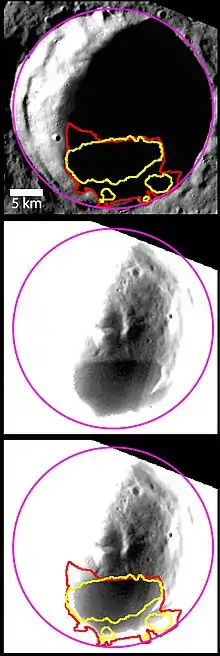
The top image shows a view of Berlioz crater, with the regions that host radar-bright material (yellow) and persistent shadows (red) identified. The middle image was acquired a few hours after the top image, using a longer exposure of the WAC broadband filter, and stretched to reveal the details within the shadowed crater. A distinctively darker region is seen on the crater's floor, which corresponds well with the radar-bright and shadowed regions (bottom image). The darker, low-reflectance material is postulated to be composed of frozen, organic-rich, volatile materials that form through a lag deposit process.[2]
 MESSENGER WAC image | |
| Planet | Mercury |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 79.36°N 321.34°W |
| Quadrangle | Borealis |
| Diameter | 31.44 km (19.54 mi) |
| Eponym | Hector Berlioz |

Berlioz crater interior
References
- "Berlioz". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. NASA. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- BURIED ICE, MESSENGER Featured Image Database
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.