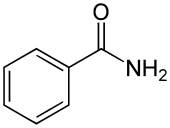
Benzamide
Benzamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula of C7H7NO. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid. In powdered form, it appears as a white solid, while in crystalline form, it appears as colourless crystals.[5] It is slightly soluble in water,[2] and soluble in many organic solvents.[6] It is a natural alkaloid found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa.[6]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzamide[1] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Benzenecarboxamide | |
| Other names
Benzoic acid amide Phenyl carboxamide Benzoylamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 385876 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.207 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 121.139 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Off-white solid |
| Density | 1.341 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 127 to 130 °C (261 to 266 °F; 400 to 403 K) |
| Boiling point | 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K) |
| 13.5 g/L (at 25°C)[2] | |
| Acidity (pKa) | |
| -72.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Pharmacology | |
| N05AL (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H341 | |
| P201, P202, P264, P270, P281, P301+P312, P308+P313, P330, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) |
| > 500 °C (932 °F; 773 K) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Chemical derivatives
A number of substituted benzamides are commercial drugs, including:
- Analgesics
- Ethenzamide
- Salicylamide
- Salverine
- procainamide
- Antidepressants
- Antiemetics/Prokinetics
- Alizapride
- Batanopride
- Bromopride
- Cinitapride
- Cisapride
- Clebopride
- Dazopride
- Itopride
- Metoclopramide
- Mosapride
- Prucalopride
- Renzapride
- Trimethobenzamide
- veralipride
- Zacopride
- Antipsychotics
- Opioids
- Others
- 3-Aminobenzamide
- aminohippuric acid
- Chidamide
- Denipride
- Entinostat
- Eticlopride
- imatinib
- Mocetinostat
- Procarbazine
- Pyramide (pyridinyl ethylbenzimide)[7]
- Raclopride
- Sunifiram
See also
- ATC code N05AL Benzamides – Therapeutic subgroup for alphanumeric classification of drugs
References
- Favre, Henri A.; Powell, Warren H. (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 841. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 9780854041824. OCLC 1077224056. Archived from the original on 2022-10-11. Retrieved 2022-10-11.
- "Benzamide | 55-21-0 supplier and manufacturer". BuyersGuideChem. Archived from the original on July 29, 2017. Retrieved October 11, 2022.
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 5–89 [sic]. ISBN 9781498754286. OCLC 1012162798. Archived from the original on 2022-10-11. Retrieved 2022-10-11. page cited is 5-89, not 5 to 89
- Bordwell, Frederick G.; Ji, Guo Zhen (October 1991). "Effects of structural changes on acidities and homolytic bond dissociation energies of the hydrogen-nitrogen bonds in amidines, carboxamides, and thiocarboxamides". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 113 (22): 8398–8401. doi:10.1021/ja00022a029. Archived from the original on 2020-12-11. Retrieved 2022-10-11.
- CID 2331 from PubChem
- "benzamide, CAS number 55-21-0". The Good Scents Company. Retrieved October 11, 2022.
- Kent, James A.; Singh, K. N.; Merchant, Kavita (2012). "The Agrochemical Industry, Annex 17.1". In Kent, James A. (ed.). Handbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnology. New York: Springer Verlag. pp. 643–698. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-4259-2_17. ISBN 9781461442592. OCLC 1097100876. Archived from the original on 2022-10-11. Retrieved 2022-10-11.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
