Mattole language
Mattole, or Mattole–Bear River, is an extinct Athabaskan language once spoken by the Mattole and Bear River peoples of northern California. It is one of the four languages belonging to the California Athabaskan cluster of the Pacific Coast Athabaskan languages. It was found in two locations: in the valley of the Mattole River, immediately south of Cape Mendocino on the coast of northwest California, and a distinct dialect on Bear River, about 10 miles to the north.
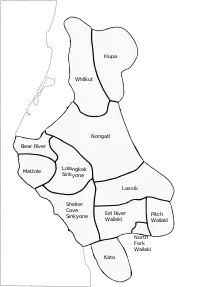
Mattole and other California Athabaskan languages.
| Mattole | |
|---|---|
| Mattole–Bear River | |
| Native to | United States |
| Region | California |
| Ethnicity | Mattole, Bear River |
| Extinct | (date missing) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | mvb |
| Glottolog | matt1238 |
 Mattole is classified as Extinct by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger [1] | |
References
- Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger (Report) (3rd ed.). UNESCO. 2010. p. 11.
- Driver, Harold Edson (1935). Vocabularies (from Tolowa, Chilula, Van Duzen, Mattole, Sinkyone of Northwestern California). California Indian Library Collections. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- Goddard, Pliny Earle (1929). "The Bear River Dialect of Athapascan." University of California Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnology 24 (5):291-334, 1929.
- Golla, Victor (2011). California Indian Languages. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-052-026667-4.
- Li, Fang-Kuei (1930). Mattole: an Athabaskan language. Publications in Anthropology, Linguistics Series. Chicago, Ill.: The University of Chicago Press.
- Yeadon, David, "California’s North Face", National Geographic, vol. 184, no. 1, p. 48-79, July 1993.
External links
- A Survey of the Athabaskan Language Mattole
- Mattole language overview at the Survey of California and Other Indian Languages
- Mattole at native-languages.org
- Mattole, World Atlas of Language Structures Online
- OLAC resources in and about the Mattole language
- Mattole basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database
- "Live Your Language Alliance (LYLA)". Retrieved 2012-08-02. "It is the desire of the Live Your Language Alliance to hear and speak the traditional languages of the Tolowa, Karuk, Yurok, Hupa, Tsnungwe, Wiyot, Mattole, and Wailaki."
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.