Bangstad syndrome
Bangstad syndrome is a severe, inherited congenital disorder associated with abnormalities of the cell membrane.
| Bangstad syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ataxia-diabetes-goiter-gonadal insufficiency syndrome |
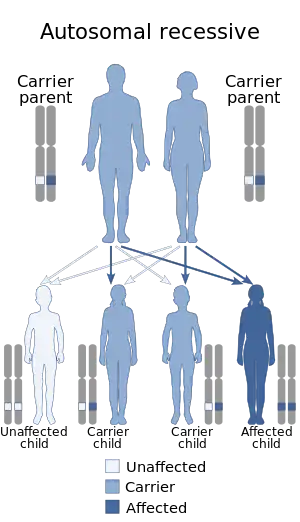 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner | |
It was characterized in 1989 by H. J. Bangstad.[1]
Presentation
Presenting at birth,[2] features of the disorder include moderately severe IUGR, microcephaly, craniosynostosis, moderately severe post-uterine growth retardation, deafness, deep-set eyes, cryptorchidism, truncal obesity and acanthosis nigricans, small teeth, prognathism, dislocated radial heads without generalized skeletal dysplasia, however, tall vertebrae, moderate mental retardation, hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, hypoparathyroidism.
Diagnosis
References
- Bangstad HJ, Beck-Nielsen H, Hother-Nielsen O, et al. (May 1989). "Primordial birdheaded nanism associated with progressive ataxia, early onset insulin resistant diabetes, goiter and primary gonadal insufficiency. A new syndrome". Acta Paediatr Scand. 78 (3): 488–93. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb11119.x. PMID 2662702. S2CID 38984786.
- Bruno Bissonnette; Igor Luginbuehl; Bernard J. Dalens (20 July 2006). Syndromes: rapid recognition and perioperative implications. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 92–. ISBN 978-0-07-135455-4. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.