Asplanchna brightwellii
Asplanchna brightwellii are a species of rotifer from the genus Asplanchna. They are known to inhabit eutrophic water.[2] The sac-like freshwater rotifier is known to eat cladocerans, protozoans, and other rotifers.[2][3] A. brightwelli are relatively large for rotifiers, transparent and ovoviviparous which makes the species ideal for morphological studies.[4]
| Asplanchna brightwellii | |
|---|---|
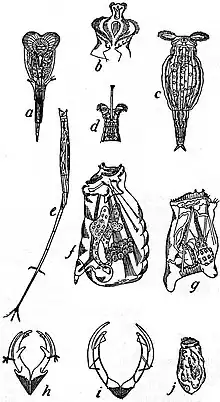 | |
| figure h is the incudate jaws of Aplanchna brightwellii | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Rotifera |
| Class: | Monogononta |
| Order: | Ploima |
| Family: | Asplanchnidae |
| Genus: | Asplanchna |
| Species: | A. brightwellii |
| Binomial name | |
| Asplanchna brightwellii | |
References
- "WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Asplanchna brightwelli Gosse, 1850". www.marinespecies.org. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- Sarma, S. S.S.; García-Martinez, Gerzon; Nandini, S. (December 2007). "Population Growth of Asplanchna brightwellii (Rotifera) Fed Prey Species Having Different Morphological Defenses". Journal of Freshwater Ecology. 22 (4): 667–676. doi:10.1080/02705060.2007.9664827. ISSN 0270-5060. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- Santos-Medrano, Gustavo Emilio; Robles-Vargas, Daniel; Hernández-Flores, Saraí; Rico-Martínez, Roberto (1 July 2017). "Life table demography of Asplanchna brightwellii Gosse, 1850 fed with five different prey items". Hydrobiologia. 796 (1): 169–179. doi:10.1007/s10750-016-3069-z. ISSN 1573-5117.
- Hochberg, Rick (April 2009). "Three-dimensional reconstruction and neural map of the serotonergic brain of Asplanchna brightwellii (Rotifera, Monogononta)". Journal of Morphology. 270 (4): 430–441. doi:10.1002/jmor.10689. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.