Annonamine
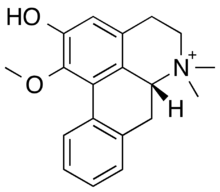
Annonamine is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid isolated from Annona muricata[1] (commonly known as soursop, graviola, guanabana, paw-paw and sirsak), a plant commonly used in folk medicine by indigenous communities in Africa and South America.[2] Structurally, it contains an aporphine core featuring a quaternary ammonium group.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(6aR)-2-Hydroxy-1-methoxy-6,6-dimethyl-5,6,6a,7-tetrahydro-4H-dibenzo[de,g]quinolin-6-ium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H22NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 296.390 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
- Asimilobine - amine not quaternized
- Anonaine
- Pukateine
References
- Matsushige, A; Kotake, Y; Matsunami, K; Otsuka, H; Ohta, S; Takeda, Y (2012). "Annonamine, a new aporphine alkaloid from the leaves of Annona muricata". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 60 (2): 257–9. doi:10.1248/cpb.60.257. PMID 22293487.
- Moghadamtousi, Soheil; Fadaeinasab, Mehran; Nikzad, Sonia; Mohan, Gokula; Ali, Hapipah; Kadir, Habsah (10 July 2015). "Annona muricata (Annonaceae): A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Isolated Acetogenins and Biological Activities". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 16 (7): 15625–15658. doi:10.3390/ijms160715625. PMC 4519917.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.