Amifloxacin
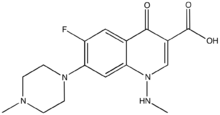
Amifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, which is similar in its activity to ciprofloxacin.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
6-Fluoro-1-(methylamino)-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.081.090 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H19FN4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 334.3 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Johnson, Juditch A.; David P. Benzinger (1985). "Metabolism and Disposition of Amifloxacin in Laboratory Animals". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 27 (5): 774–781. doi:10.1128/aac.27.5.774. PMC 180151. PMID 4015071.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.