Acropectoral syndrome
Acropectoral syndrome is an autosomal dominant skeletal dysplasia syndrome affecting the hands, feet, sternum, and lumbosacral spine. A recently proposed candidate gene for preaxial polydactyly is LMBR1, encoding a novel transmembrane receptor, which may be an upstream regulator of SHH.[1] The LMBR1 gene is on human chromosome 7q36.[2]
| Acropectoral syndrome | |
|---|---|
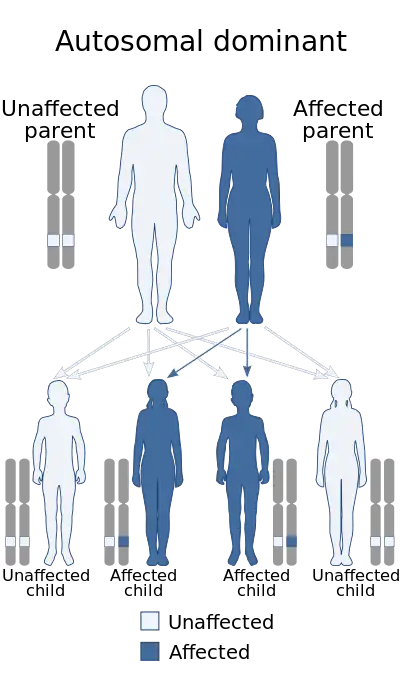 | |
| Acropectoral syndrome has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. |
Presentation
Some individuals have preaxial polydactyly in the feet (unilateral in one, bilateral in 13), consisting of a small extra biphalangeal toe, in most cases with an associated rudimentary extra metatarsal, lying in a soft tissue web between the hallux and second toe. In some cases, this was accompanied by hypoplasia of the head of the first metatarsal and absence of both phalanges of the hallux. [1]
Genetics
The cytogenetic location is 7q36 and genomic coordinates are GRCh37:147,900,000 - 159,138,663 (NCBI). Mapping of this syndrome was done by Dundar and coworkers in 2001. They showed that this phenotype was linked to a 6.4-cM region of 7q36 flanked by the EN2 gene and the marker D7S2423. Dundar and coworkers characterized and mapped acropectoral syndrome and also showed it was unrelated to acropectorovertebral syndrome. The mapping showed that the acropectoral locus was in a region where preaxial polydactyly and triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly had previously been mapped. This study was important because it expanded the range of phenotypes that are connected to this locus. Previously, preaxial polydactyly and sternal defects have been linked to ectopic expression of the gene Sonic hedgehog Shh in limbbud and lateral plate mesoderm during development in mice. Dundar and coworkers found that the LMBR1 gene links to pre axial polydactyly. This gene encodes for a new transmembrane receptor and it is proposed that this receptor is an upstream regulator of SHH.[1]
Diagnosis
Society
Three main support groups of this syndrome are the ASGA in Australia, The Association for Children with Genetic Disorders in Poland, and the Association of People of Genetic Disorders in Greece.
References
- Dundar M, Gordon TM, Ozyazgan I, et al. (May 2001). "A novel acropectoral syndrome maps to chromosome 7q36". J. Med. Genet. 38 (5): 304–9. doi:10.1136/jmg.38.5.304. PMC 1734869. PMID 11333865.
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 605967