52nd parallel north
The 52nd parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 52 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
.svg.png.webp)
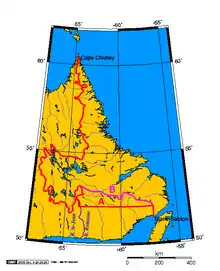
In Canada, part of the legally defined border between Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador is defined by the parallel, though Quebec maintains a dormant claim to some of the territory north of this line.[1]
The catchment area of London, the capital city of England and the United Kingdom, can be broadly defined by the 51st and 52nd parallels.
At this latitude the sun is visible for 16 hours, 44 minutes during the summer solstice and 7 hours, 45 minutes during the winter solstice.[2]
Around the world

Starting at the Prime Meridian (just west of the village of Barkway in Hertfordshire, England) and heading eastwards, the parallel 52° north passes through:
See also
References
- Jacobs, Frank (2012-07-10). "Oh, (No) Canada!". Opinionator: Borderlines. The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2019-10-01. Retrieved 2012-09-23.
- "Duration of Daylight/Darkness Table for One Year". United States Naval Observatory. 2019-09-24. Archived from the original on 2019-10-12. Retrieved 2021-03-10.
- "52° North: a tangible timeline". TU Delft. Retrieved 2019-05-29.
