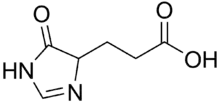
Imidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid
Imidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of histidine. It is a colorless compound that is sensitive to light in air. The compound features an imidazolone ring.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-(5-Oxo-1,4-dihydroimidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Imidazol-4-one-5-propionic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 156.139 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Occurrence
It arises via the action of urocanase on urocanic acid. Hydrolysis of the heterocycle to the glutamic acid derivative is catalyzed by imidazolonepropionate hydrolase.
Microbial production of imidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid in the human gut has been shown to affect insulin signaling, which is relevant to type II diabetes.[2]
References
- Hassall, H.; Greenberg, D. M. (1971). "Preparation and properties of 4(5)-imidazolone-5(4)-propionic acid". Methods Enzymol. 17(Pt. B): 89–91. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(71)17014-0.
- Koh, Ara; Molinaro, Antonio; Ståhlman, Marcus; Khan, Muhammad Tanweer; Schmidt, Caroline; Mannerås-Holm, Louise; Wu, Hao; Carreras, Alba; Jeong, Heeyoon; Olofsson, Louise E.; Bergh, Per-Olof; Gerdes, Victor; Hartstra, Annick; De Brauw, Maurits; Perkins, Rosie; Nieuwdorp, Max; Bergström, Göran; Bäckhed, Fredrik (2018). "Microbially Produced Imidazole Propionate Impairs Insulin Signaling through mTORC1". Cell. 175 (4): 947–961.e17. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.055. PMID 30401435. S2CID 53229780.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.