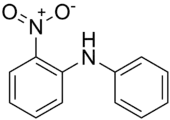
2-Nitrodiphenylamine
2-Nitrodiphenylamine, also called NDPA, 2-NDPA, 2NO2DPA, Sudan Yellow 1339, C.I. 10335, CI 10335, phenyl 2-nitrophenylamine, 2-nitro-N-phenylaniline, or N-phenyl-o-nitroaniline, is an organic chemical, a nitrated aromatic amine, a derivate of diphenylamine. Its chemical formula is C12H10N2O2, or C6H5NHC6H4NO2. It is a red crystalline solid, usually in form of flakes or powder, with melting point of 74-76 °C and boiling point of 346 °C. It is polar but hydrophobic.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Nitro-N-phenylaniline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.953 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1661 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 214.224 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 74 to 75 °C (165 to 167 °F; 347 to 348 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2-Nitrodiphenylamine is used as a stabilizer for synthetic rubbers, explosives, propellants (e.g. in Otto fuel II, smokeless powders, in some US Army double-base propellants in solid rockets, and in other applications involving nitric acid esters), plastics, and lubricants. It is also an intermediate for organic synthesis, and a civilian solvent dye.
In some explosives, it is used to control the explosion. One of its major uses is to control the explosion rate of propylene glycol dinitrate.
As a stabilizer, its major role is to eliminate the acidic nitrates and nitrogen oxides produced by gradual decomposition of nitric acid esters, which would otherwise autocatalyze further decomposition. Its amount is usually 1-2% of the mixture; higher amounts than 2% degrade the propellant's ballistic properties. The amount of the stabilizer depletes with time; remaining content of less than 0.5% (with initial 2% content) requires increased surveillance of the munition, with less than 0.2% warranting immediate disposal, as the depletion of the stabilizer may lead to autoignition of the propellant.[1]
Other stabilizers of a similar nature are 4-nitrodiphenylamine, N-nitrosodiphenylamine. While N-methyl-p-nitroaniline (MNA also used in IMX-101), and diphenylamine (DPA) are more commonly employed.[2]
References
- "2-Nitrodiphenylamine (O-Nitro-N-Phenylaniline)".
- "PROPELLANT STABILIZERS". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-06-07.