< Cell Biology < Cytoskeleton 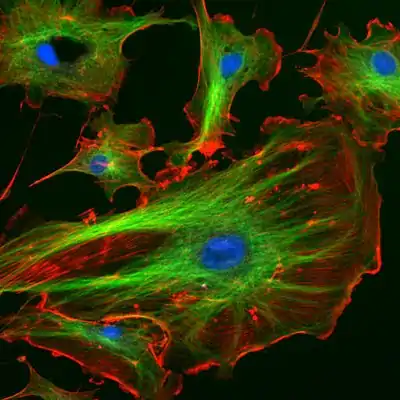
Cytoskeleton

The eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Actin filaments are shown in red, microtubules in green, and the nuclei are in blue.
Cytoskeleton is the skeleton of the cell, constructed from proteins. They lie on cytoplasm, defining cell's shape, movement and many other functions. There are 3 types of them which we will discuss shortly.
Actin filaments

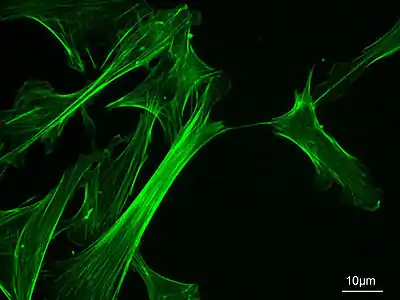
Actin cytoskeleton of mouse embryo fibroblasts, stained with Fluorescein isothiocyanate-phalloidin
Actin filaments are strings anchored one end in the plasma membrane. They generates contractile forces, which helps the cell moves and changes shape.
Actin filaments are also called microfilaments because they are the thinnest in cytoskeleton family.
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.