< A-level Mathematics < AQA 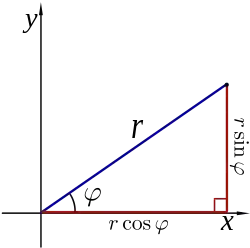
Series and limits
Two important limits:
for any real number k
for all k > 0
The basic series expansions
Improper intergrals
The integral : is said to be improper if
- the interval of integration is infinite, or;
- f(x) is not defined at one or both of the end points x=a and x=b, or;
- f(x) is not defined at one or more interior points of the interval .
Polar coordinates

A diagram illustrating the relationship between polar and Cartesian coordinates.
The area bounded by a polar curve
For the curve
r must be defined and be non-negative throughout the interval
Numerical methods for the solution of first order differential equations
Euler's formula
The mid-point formula
The improved Eular formula
where
and
Second order differential equations
Euler's identity
When substituting into the identity gives
Further reading
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.